Why does it seem like the “I” storms are always the worst hurricanes, present the most historic damage and yield the most retired names?
It’s complicated, and there are competing schools of thought.
First, it’s important to understand that the World Meteorological Organization has an international committee to govern this process under a strict procedure.
The basic principle to assess a name’s retirement is if the storm was “so deadly or costly that the future use of its name on a different storm would be inappropriate for obvious reasons of sensitivity.”
Get top local stories in DFW delivered to you every morning. >Sign up for NBC DFW's News Headlines newsletter.
So, back to the question, what is it with the “I” name?
The “I” name falls in the ninth position on the WMO’s list of storm names for the Atlantic basin, no matter the year.
These storms, simply based on climatology, will, generally, develop at a time in the season when conditions are prime.
U.S. & World
Now, “prime” conditions certainly represent a broad assumption, but let me frame it in the context that an average season in the Atlantic Basin has 14 named storms.
Continuing, on average, the fifth named storm forms in mid-to-late August, the seventh around the first of September and the ninth? It will have usually formed by the 16th of September.
Still, no season is the same and storm development doesn’t often occur on a smooth curve.
In fact, in the Atlantic Basin, much of our activity is “backloaded” to the period between mid-August to early November.
But if the peak of the season occurs around September 10th and the “I” name is the ninth name used, this lines up, right?
In essence, conditions are typically prime for hurricane development when “I” is reached on the list of storms.
Seems to makes sense as a quick explanation.
But is that the actual reason?
Brian McNoldy, a senior hurricane research associate at the University of Miami, addressed this in a recent blog post.
He found that it’s far, far simpler explanation.
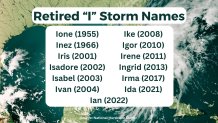
The reason “I” names are the most frequently retired is (mostly) just luck.
Yes, just luck.
He states that, “If it was related to the time of year then “H” and “J” storms should be pretty high, too.”
Since 1953, six “H” storms and five “J” storms have been retired.
Blazing past them is “F” with 10 retirements in the last several decades.
McNoldy notes that, of the 13 “I” storms that have been retired over the last 70 years, seven of them have been retired in the last 14 years.
Yep, more than half since 2008.
I hypothesize that another likely reason Florida residents have bad reactions to any “I” storm can be traced back to their experiences.
If you’re a long time local or recent relocator, perhaps you’ve tangoed with some infamous “I” storms yourself.
While Idalia is on the map today, it wasn’t so long ago that we were shaken by Ian (2022), Irma (2017) and Ivan (2004).
While “I” has proven to be a curse to Florida over the last several years, it’s just our bad luck.



