As of Friday, at least five states had active measles outbreaks, and Texas had the largest, with 400 cases.
The U.S. has already had more measles cases this year than in all of 2024, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said. Other states with outbreaks — defined as three or more cases — include New Mexico, Kansas, Ohio and Oklahoma. Since February, two unvaccinated people have died from measles-related causes.
Watch NBC 5 free wherever you are
The new outbreaks confirm health experts' fears that the virus will take hold in other U.S. communities with low vaccination rates and that the spread could last a year. The World Health Organization said this week that cases in Mexico are linked to the Texas outbreak.
Measles is caused by a highly contagious virus that is airborne and spreads easily when an infected person breathes, sneezes, or coughs. It is preventable through vaccines and has been considered eliminated from the U.S. since 2000.
Get top local stories in DFW delivered to you every morning with NBC DFW's News Headlines newsletter.
Here's what else you need to know about measles in the U.S.
How many measles cases are there in Texas and New Mexico?
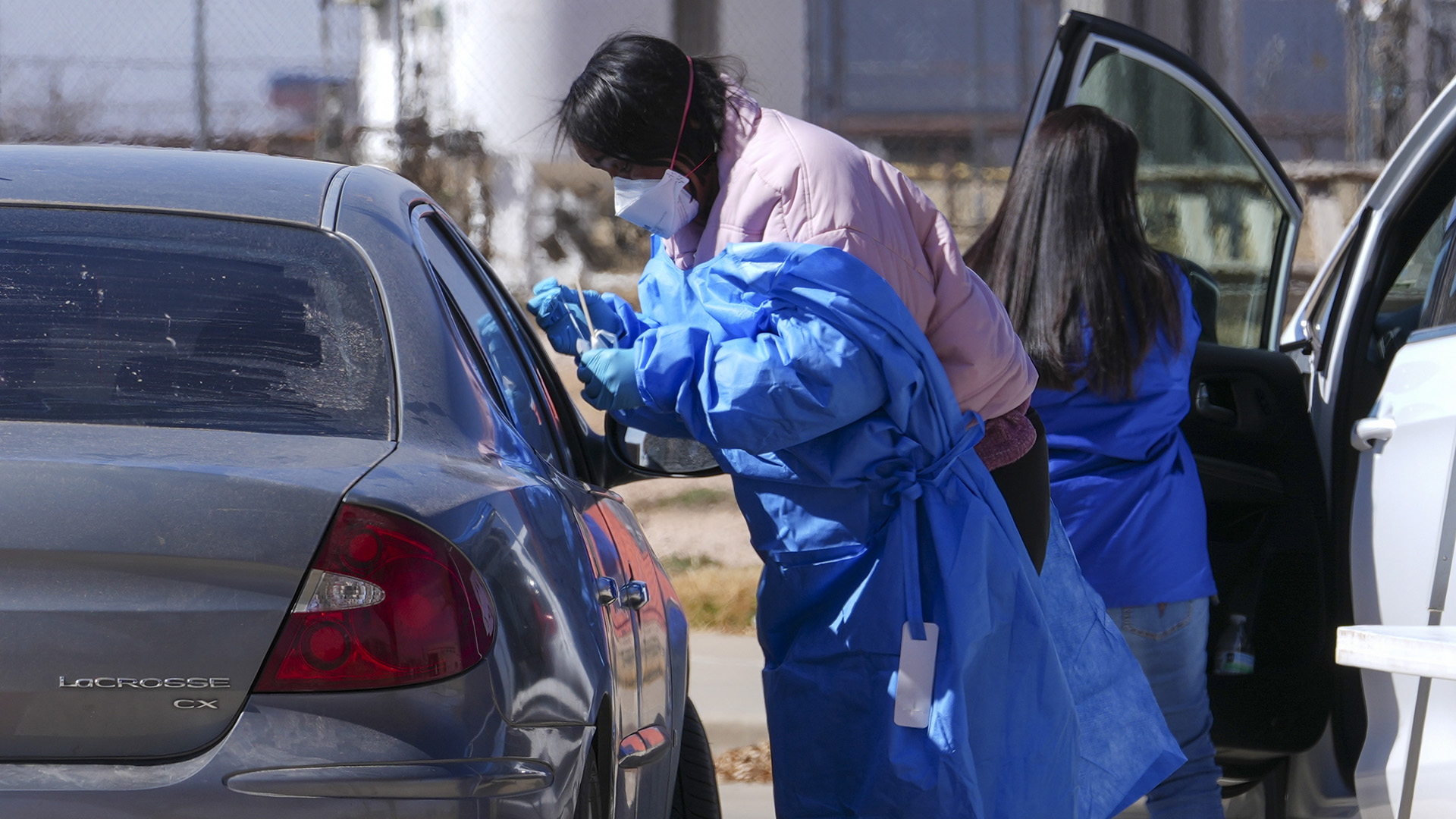
Texas' outbreak began two months ago. State health officials said Friday there were 73 new cases of measles since Tuesday, bringing the total to 400 across 17 counties — most in West Texas. Forty-one people have been hospitalized since the outbreak began, and Andrews and Midland counties were new to the list.
New Mexico announced one new case Friday, bringing the state’s total to 44. New Mexico health officials say the cases are linked to Texas' outbreak based on genetic testing. Most are in Lea County, where two people have been hospitalized, and two are in Eddy County.
A school-age child died of measles in Texas in late February, and New Mexico reported its first measles-related death in an adult on March 6.
MEASLES
How many measles cases are there in Kansas?
Kansas has 23 cases in six counties in the southwest part of the state. Kiowa and Stevens counties have six cases each, while Grant, Morton, Haskell and Gray counties have five or fewer.
The state's first reported case, identified in Stevens County on March 13, is linked to the Texas and New Mexico outbreaks based on genetic testing, a state health department spokesperson said. But health officials have not determined how the person was exposed.
How many measles cases are there in Oklahoma?
Oklahoma stayed steady at nine cases this week — seven confirmed and two probable cases. The state health department said the first two probable cases were “associated” with the West Texas and New Mexico outbreaks.
A state health department spokesperson confirmed measles exposures in Tulsa and Rogers counties but wouldn't say which counties had cases.
How many measles cases are there in Ohio?
Ohio has 10 measles cases in Ashtabula County in the northeast corner of the state, nine of those newly reported this week. The first case was in an unvaccinated adult who had interacted with someone who had traveled internationally.
In central Ohio, Knox County officials are tracing exposures from people who visited while contagious with measles. A measles outbreak in central Ohio sickened 85 in 2022.
Where else is measles showing up in the U.S.?
Measles cases also have been reported in Alaska, California, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Maryland, Michigan, Minnesota, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Tennessee, Vermont, and Washington.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention defines an outbreak as three or more related cases. As of Friday, the agency counted five clusters that qualified as outbreaks in 2025.
In the U.S., cases and outbreaks are generally traced to someone who caught the disease abroad. It can then spread, especially in communities with low vaccination rates. In 2019, the U.S. saw 1,274 cases and almost lost its status of having eliminated measles.
Do you need an MMR booster?
The best way to avoid measles is to get the measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) vaccine. The first shot is recommended for children between 12 and 15 months old and the second between 4 and 6 years old.
People at high risk for infection who got the shots many years ago may want to consider getting a booster if they live in an area with an outbreak, said Scott Weaver with the Global Virus Network, an international coalition. Those may include family members living with someone who has measles or those especially vulnerable to respiratory diseases because of underlying medical conditions.
Adults with “presumptive evidence of immunity” generally don’t need measles shots now, the CDC said. Criteria include written documentation of adequate vaccination earlier in life, lab confirmation of past infection or being born before 1957, when most people were likely to be infected naturally.
A doctor can order a lab test called an MMR titer to check your levels of measles antibodies, but health experts don't always recommend this route and insurance coverage can vary.
Getting another MMR shot is harmless if there are concerns about waning immunity, the CDC said.
People who have documentation of receiving a live measles vaccine in the 1960s don’t need to be revaccinated, but people who were immunized before 1968 with an ineffective measles vaccine made from “killed” virus should be revaccinated with at least one dose, the agency said. That also includes people who don’t know which type they got.
What are the symptoms of measles?
Measles first infects the respiratory tract, then spreads throughout the body, causing a high fever, runny nose, cough, red, watery eyes and a rash.
The rash generally appears three to five days after the first symptoms, beginning as flat red spots on the face and then spreading downward to the neck, trunk, arms, legs and feet. When the rash appears, the fever may spike over 104 degrees Fahrenheit, according to the CDC.
Most kids will recover from measles, but infection can lead to dangerous complications such as pneumonia, blindness, brain swelling and death.
How can you treat measles?
There’s no specific treatment for measles, so doctors generally try to alleviate symptoms, prevent complications and keep patients comfortable.
What is measles?
Measles is a respiratory virus that can survive in the air for up to two hours. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, up to nine out of 10 people who are susceptible will get the virus if exposed.
Most kids will recover from measles if they get it, but infection can lead to dangerous complications like pneumonia, blindness, brain swelling, and death.
Is the vaccine safe?
Yes, the measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) vaccine is safe and highly effective in preventing measles infection and severe cases of the disease.
The first shot is recommended for children between 12 and 15 months old, and the second for children between 4 and 6 years old. The vaccine series is required for kids before kindergarten in public schools nationwide.
Before the vaccine was introduced in 1963, the U.S. saw some 3 million to 4 million cases per year. Now, there are usually fewer than 200 in a normal year.
There is no link between the vaccine and autism, despite a now-discredited study and health disinformation.
Why do vaccination rates matter?
In communities with high vaccination rates — above 95% — diseases like measles have a harder time spreading through communities. This is called “herd immunity.”
But childhood vaccination rates have declined nationwide since the pandemic and more parents are claiming religious or personal conscience waivers to exempt their kids from required shots.
The U.S. saw a rise in measles cases in 2024, including an outbreak in Chicago that sickened more than 60. Five years earlier, measles cases were the worst in almost three decades in 2019.
Gaines County has one of the highest rates in Texas of school-aged children who opt out of at least one required vaccine, with nearly 14% of K-12 children in the 2023-24 school year. Health officials said that number is likely higher because it doesn’t include many children who are homeschooled and whose data would not be reported.
What are public health officials doing to stop the spread?
Health workers are hosting regular vaccination clinics and screening efforts in Texas, as well as working with schools to educate people about the importance of vaccination and offering shots.